
Tap-based and contactless interactions
Faster data transfer

Low-power, secure, short-range communication

Integration with Connected Products and IoT
In an era where products, systems, and services are expected to be faster, safer, and more intuitive than ever, Near Field Communication (NFC) has emerged as a strategic enabling technology. Beyond consumer applications like mobile wallets, NFC is rapidly becoming foundational in how devices interact securely and seamlessly in enterprise and industrial environments.
The global NFC ecosystem reflects this shift. In 2024, the NFC market was valued at approximately USD 29.9–43.5 billion, and it is forecasted to continue expanding rapidly through the next decade, with projected growth reaching upward of USD 94 billion by 2030 or even over USD 100 billion by 2033, depending on market forecasts.
This growth trajectory is underpinned by two crucial trends:
These factors are redefining how products identify users, trigger actions, and integrate into broader digital infrastructures – making NFC a cornerstone of modern connected product design rather than just a consumer convenience.

Modern products and systems are expected to offer instantaneous, secure, and frictionless interactions. Legacy approaches relying on manual entry, physical keys or visual codes (like QR) introduce clear operational bottlenecks:
Across industries, from access control to asset identification and payment terminals to configuration workflows, these challenges hinder both user experience and system scalability.
Tap-based and contactless interactions enabled by NFC address these operational pain points by delivering:
For example, adoption of NFC-enabled contactless payments surged after the COVID-19 pandemic, with contactless transaction counts in the U.S. reaching nearly 18 billion in 2023 and around 61 % of consumers indicating a preference for contactless payment options for reasons of convenience and hygiene.
This preference for contactless experiences underscores a broader trend: NFC isn’t just a consumer convenience; it’s a product engineering enabler that directly supports digital transformation goals like automation, security, and seamless human-machine interaction.
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows devices to exchange data over very short distances – typically within a few centimetres. It operates on a globally standardized radio frequency (13.56 MHz) and enables intentional, proximity-based interactions between compatible devices.
At its core, NFC builds on principles of RFID and is optimized for:
Unlike visual code approaches (e.g., QR), which rely on optical scanning, NFC allows devices themselves to initiate communication, enabling more seamless and secure interactions across diverse environments.
In this mode, devices read and write data to NFC tags. Typical use cases include:
This mode empowers objects with digital intelligence, facilitating workflows that are faster, more automated, and less error-prone.
Peer-to-peer enables direct device-to-device data exchange. This supports secure sharing of information during:
ePaper technology is a breakthrough for low-power, information-centric applications. Key advantages include:
This makes ePaper ideal for IoT devices, industrial dashboards, retail signage, battery-powered sensors, logistics labels, and smart infrastructure where power efficiency and readability are paramount.
NFC serves as a gateway between the physical and digital worlds, especially in connected products and IoT ecosystems.
It enables physical objects to:
Passive NFC tags are small, low-cost chips that can be attached to almost any physical object, giving it a contextual digital identity that can be read by compatible devices. This fundamental capability supports everything from asset tracking and configuration to secure interaction logging and user validation.
With continued NFC adoption in wearables, smartphones, and industrial devices, the technology is increasingly becoming the entry point for broader IoT integrations, enabling smarter, more responsive systems.
One of NFC’s core strengths lies in its inherent security characteristics:
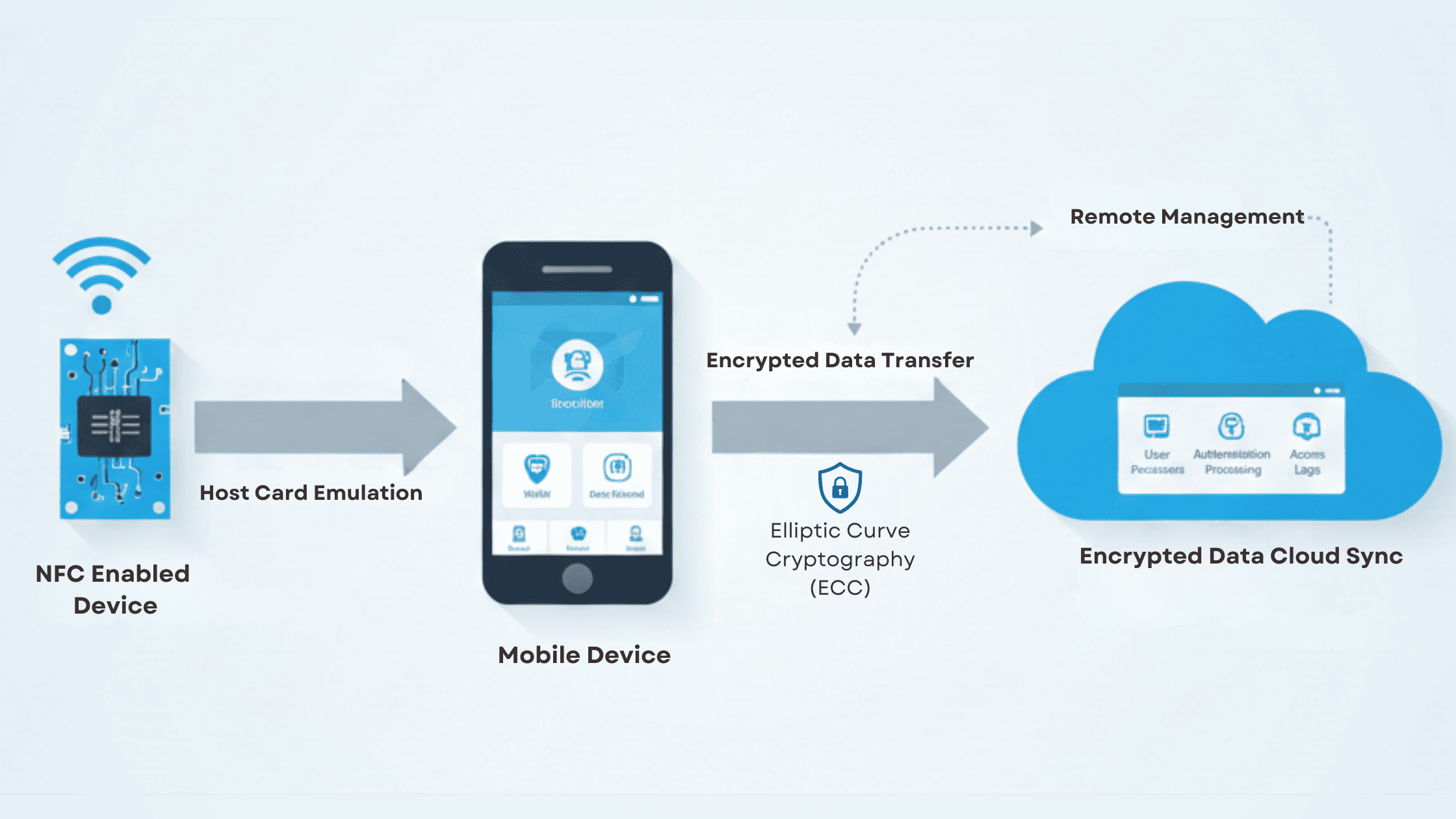
However, when NFC capabilities are moved from dedicated hardware (e.g., secure elements) to software-based implementations (e.g., Host Card Emulation – HCE), additional security considerations emerge. Well-engineered NFC systems must incorporate layered security, including encryption, device identity, and secure execution environments, to maintain robust protection across use cases.
In conventional designs, credentials are stored in a secure element (SE) – a tamper-resistant hardware component designed to safeguard sensitive keys and data. This approach offers high security but can be less flexible for rapid iteration and integration with modern software stacks.
HCE decouples the credential storage from the secure hardware element, hosting virtual card applications on the device’s operating system instead. This enables:
However, HCE introduces new risks such as OS-level vulnerabilities and malware threats, which must be mitigated through layered security measures like white-box cryptography, trusted execution environments, and tokenization.
At Alpha ICT, NFC is not treated as a standalone feature – it’s woven into end-to-end product engineering to ensure that contactless capabilities deliver real operational value.
Key Capabilities Alpha ICT Brings to NFC Adoption:
By combining deep engineering proficiency with rigorous security practices, Alpha ICT ensures that NFC is a strategic enabler for connected products, not just an added feature.
Near Field Communication has moved well beyond consumer mobile payments to become a foundational technology across industries. Its capability to enable secure, fast, contactless interactions within tightly controlled proximity makes it indispensable in modern product design, access systems, and IoT ecosystems.
For product companies aiming to deliver differentiated value, the choice isn’t simply whether to adopt NFC; it’s how to engineer it effectively and securely. Partnering with Alpha ICT’s experienced engineering team ensures NFC implementations that strike the right balance between security, usability, and scalability, unlocking the full potential of contactless intelligence.